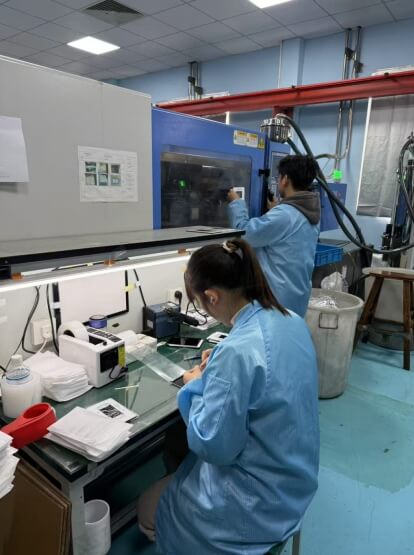
IMD Process and Materials Explanation
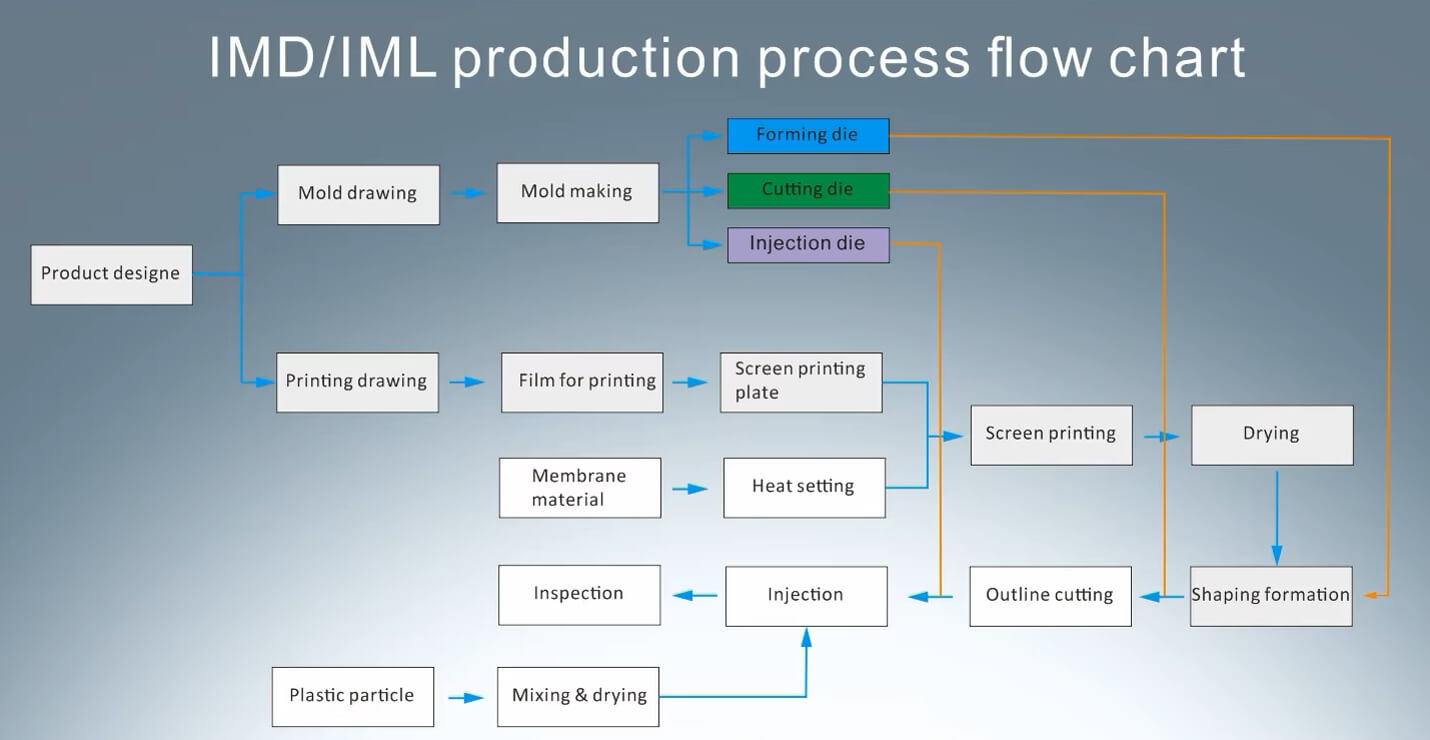
IMD process flow
An sophisticated manufacturing technique called IMD (In-Mold Decoration) incorporates functional components, decorative patterns, and textures straight into the injection molding process. The specific steps of the IMD procedure are listed below:
Process Overview
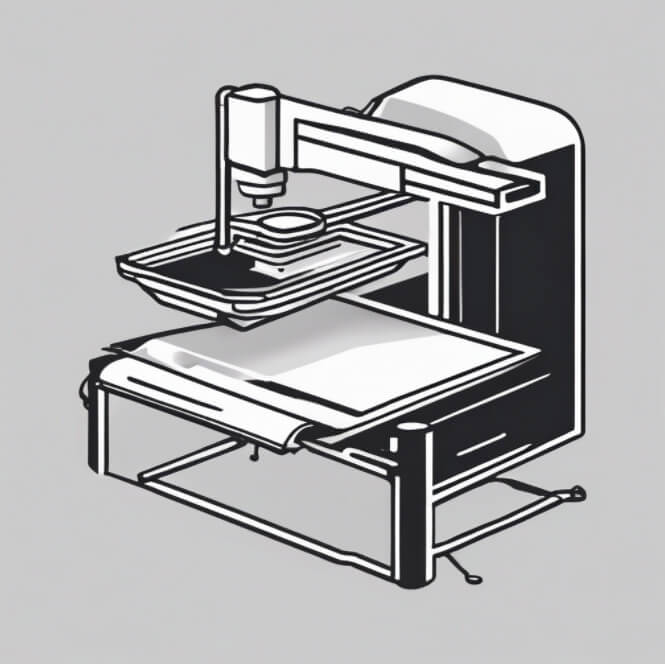 1. Silk printing
1. Silk printing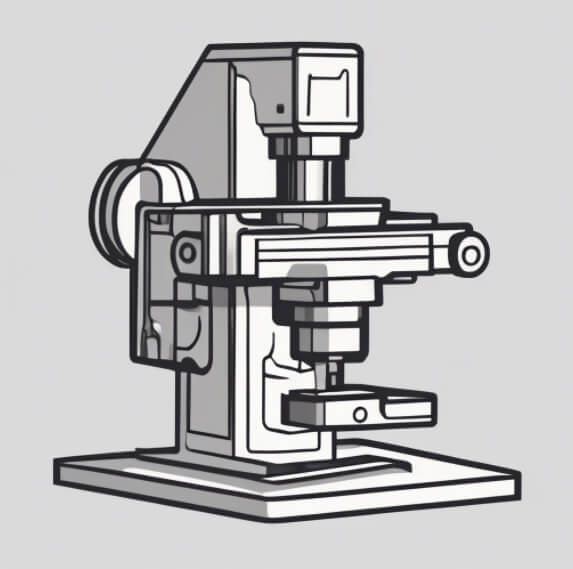 2. Die cutting
2. Die cutting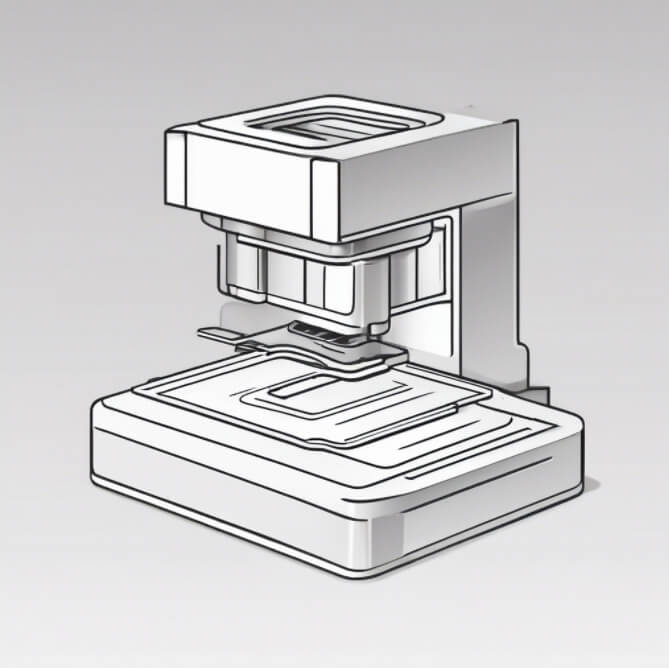 3. Forming
3. Forming 4. Plastic injection
4. Plastic injection
Manufacturing steps
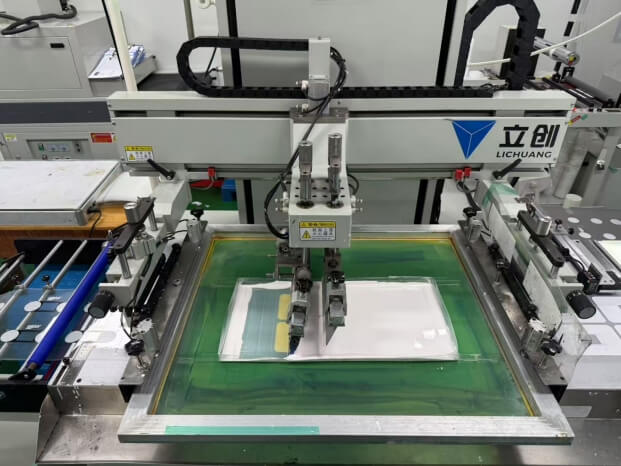
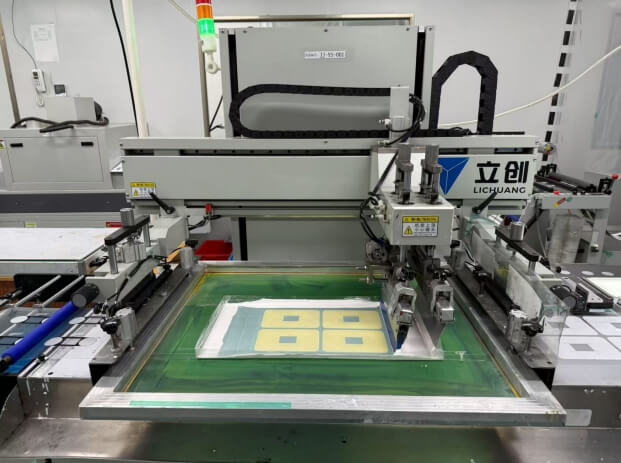
1. Printing
Design the graphics and text according to the product requirements
Screen printing/offset printing/digital printing are adopted
The technology prints the patterns on films such as PET


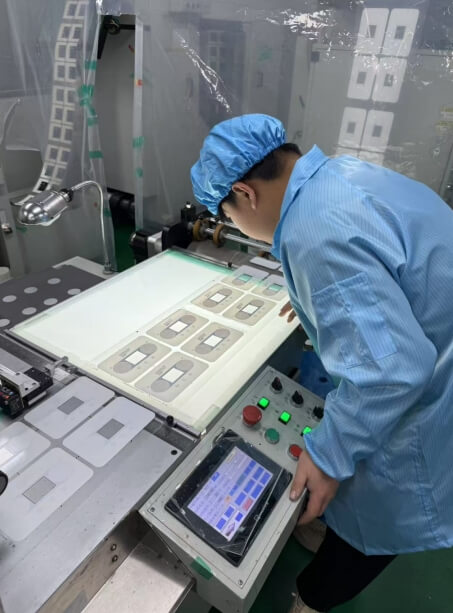
2. Printing inspection
Semi-finished product inspection during the printing process

3. Drying
Drying and curing treatment is required to ensure the stability of the ink and the flatness of the film
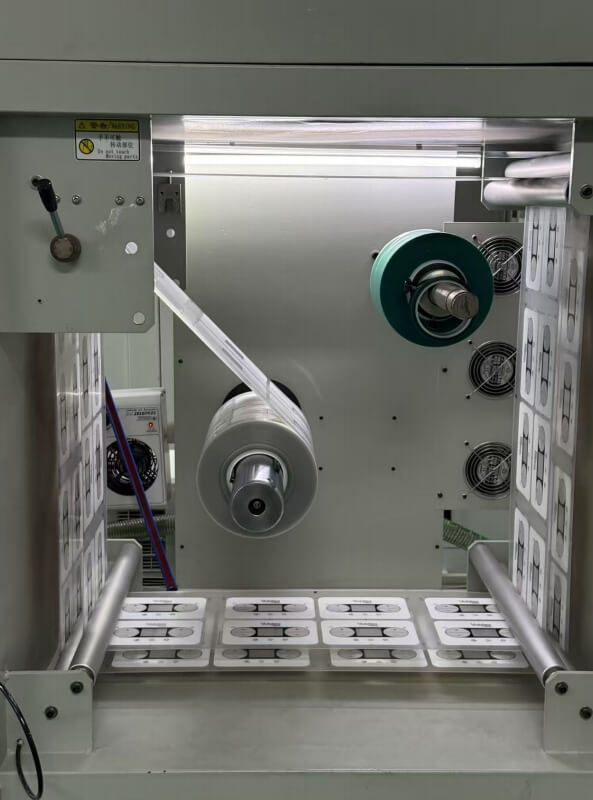

4. Diaphragm punching
The shape of the punching diaphragm
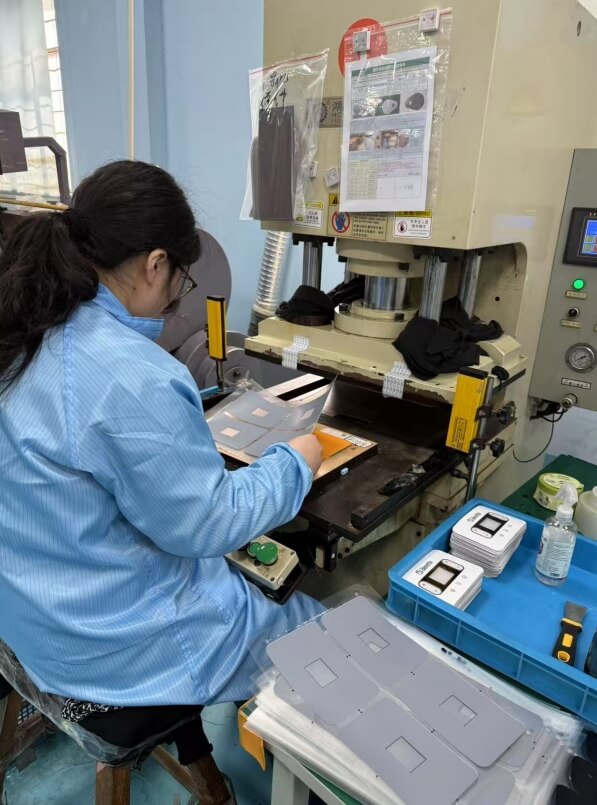

5. Hot pressing forming
Place the printed film into the mold and make it adhere to the mold cavity through high-pressure gas or mechanical pressure to form a 3D shape.
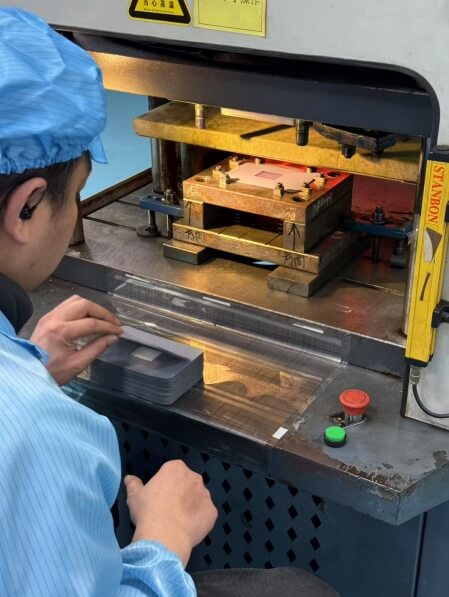

6. Injection molding
Place the formed film into the cavity of the injection mold and fix it by a mechanical hand or manually to ensure that the film is closely attached to the mold. Molten plastics (such as PC, ABS) are injected into the mold and combined with the diaphragm to form an integrated product.
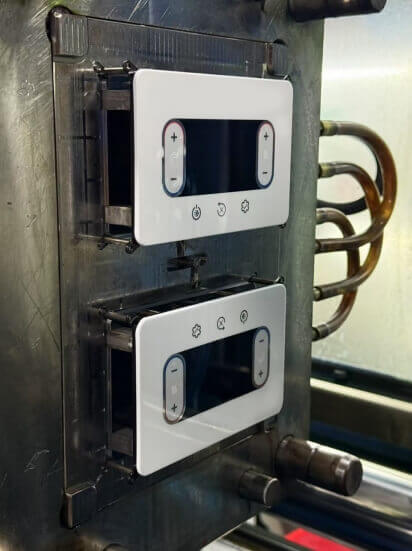

7. Final Product
After being decorated, the product is released from the mold and prepared for is ready for quality control.

Optional materials & performance characteristics
A range of materials are used in the IMD process to accomplish particular performance goals. A thorough comparison of materials frequently utilized in IMD manufacture may be found below:
|
Material |
Picture |
Key Properties |
Typical Applications |
|
PC (Polycarbonate) |
 |
High impact resistance, excellent transparency, and heat resistance. |
Automotive dashboards, electronic device panels. |
|
PMMA (Acrylic) |
 |
High optical clarity, scratch resistance, and UV stability. |
Transparent panels, display covers. |
|
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) |
 |
Excellent chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and recyclability. |
Food packaging, labels, and touch panels. |
|
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) |
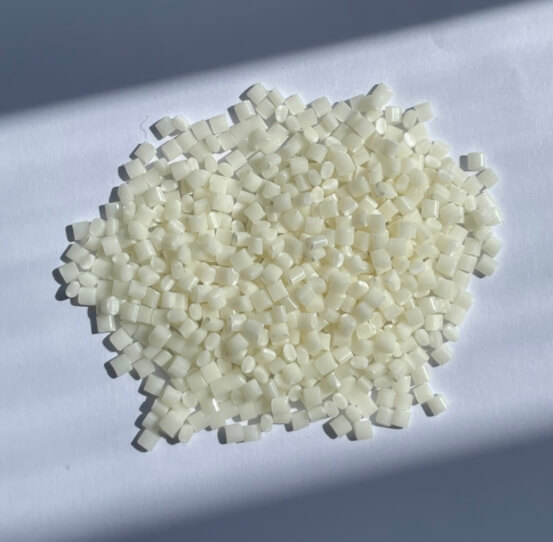 |
Good toughness, impact resistance, and easy processing. |
Consumer electronics, automotive interior parts. |